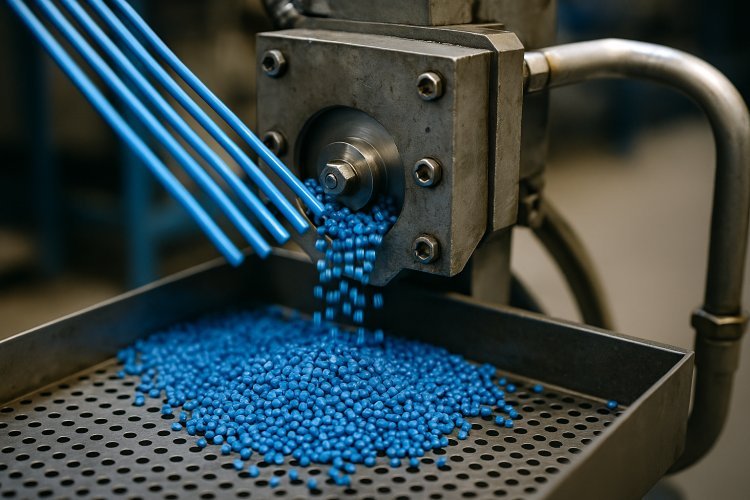
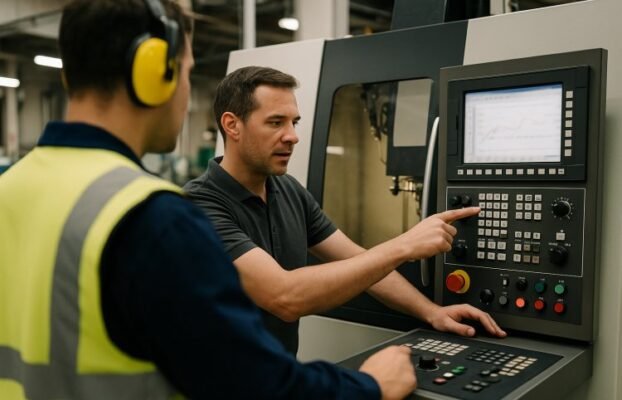
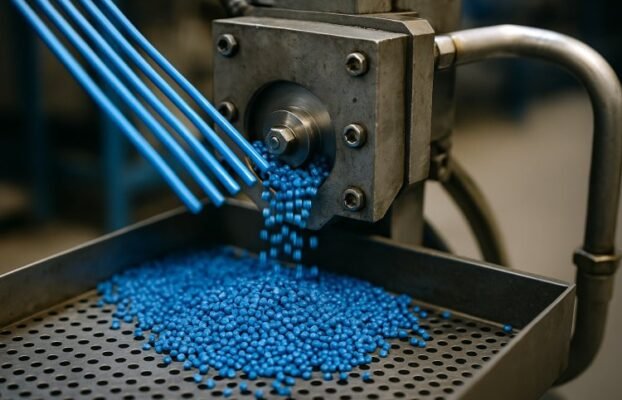
Masterbatch manufacturing requires specialized equipment for consistent quality and efficient production. Essential machines include twin-screw extruders for compounding, precision feeding systems for material dosing, pelletizing equipment for final product formation, and auxiliary systems for process control. Modern facilities integrate automated control systems with core processing equipment to optimize throughput rates while maintaining quality standards.
TL;DR
- Twin-screw extruders serve as the core compounding machine for material mixing
- Gravimetric feeders provide superior dosing accuracy compared to volumetric systems
- Pelletizing systems determine final pellet shape, size, and quality characteristics
- High-speed mixers prepare materials before extrusion processing
- Automated control systems enable recipe management and process optimization
- Auxiliary equipment maintains consistent production conditions throughout the line
Critical Factors in Masterbatch Equipment Selection
Production capacity drives equipment sizing decisions to match throughput rate specifications with expected demand. Material characteristics significantly influence machine selection. High-viscosity filler masterbatches require higher torque extruders than standard color masterbatches.
Quality requirements determine precision levels needed across feeding, mixing, and pelletizing systems. Budget constraints require balancing capital investment against operational efficiency. A well-planned production line strategy ensures components work together efficiently, preventing bottlenecks and maximizing system performance.

Essential Machines for Masterbatch Manufacturing
The global masterbatch market reached USD 6.60 billion in 2024 and continues growing at 6.6% annually through 2030 [1], driving demand for efficient manufacturing equipment. Each machine category serves a critical function in the production process.
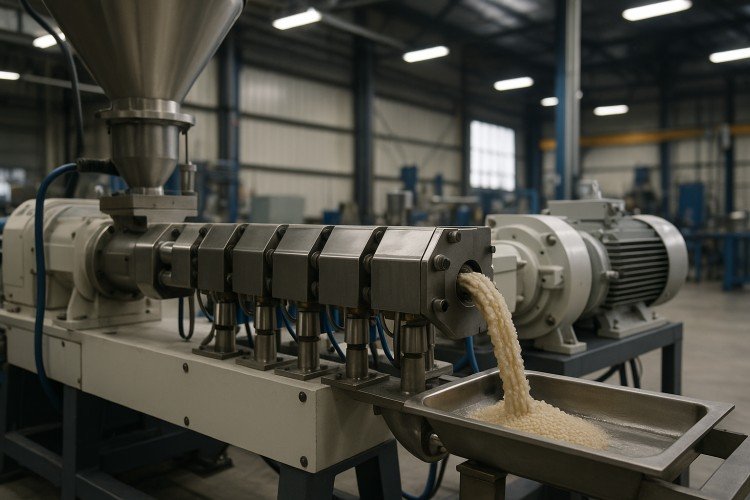
Twin-Screw Extruder (TSE)
The twin-screw extruder functions as the heart of masterbatch manufacturing operations. Co-rotating twin-screw extruders dominate the industry due to superior mixing capabilities and self-cleaning properties. These machines feature intermeshing screws that rotate in the same direction, creating powerful dispersive and distributive mixing. The U.S. twin-screw extruder market reached USD 478.5 million in 2024 [2], reflecting strong demand from the plastics and pharmaceutical industries. Counter-rotating twin-screw extruders serve specialized applications requiring gentle processing of shear-sensitive materials.
L/D ratio selection impacts mixing efficiency and residence time. Standard masterbatch production typically uses L/D ratios between 32 and 48. Higher L/D ratios provide more mixing zones for complex formulations requiring extensive pigment dispersion. Screw geometry can be customized through modular elements. Manufacturers configure kneading blocks, conveying elements, and mixing sections based on specific material requirements.
Torque capacity determines the extruder’s ability to process highly filled compounds. Filler masterbatches containing up to 80% CaCO₃ demand high-torque gearboxes. Temperature control across multiple barrel zones ensures proper plasticization while preventing thermal degradation. Vacuum degassing ports remove moisture and volatiles during compounding extrusion.

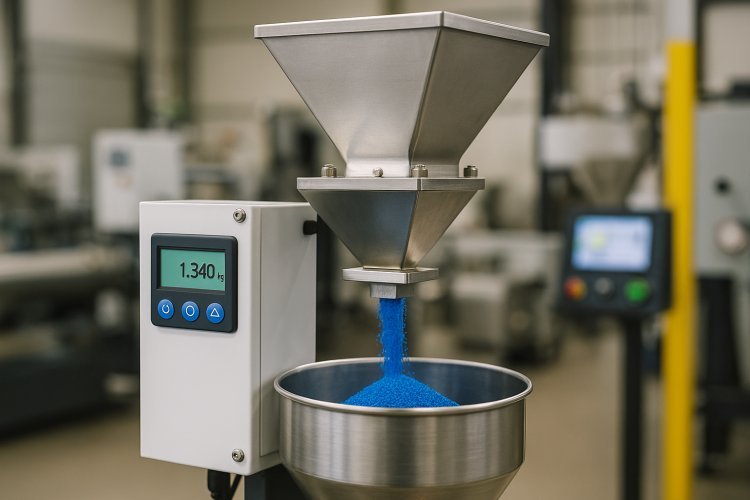
Feeding Systems
Feeding systems control the precise introduction of carrier resin, pigments, and additives into the extruder. Gravimetric feeders measure material weight continuously, providing ±0.2% accuracy. These loss-in-weight systems automatically adjust motor speed to maintain consistent flow regardless of bulk density variations.
Volumetric feeders offer economical alternatives for less stringent precision requirements, typically achieving ±5% accuracy. Side feeders enable split-feed processing, where heat-sensitive additives enter downstream of the main melting zone.
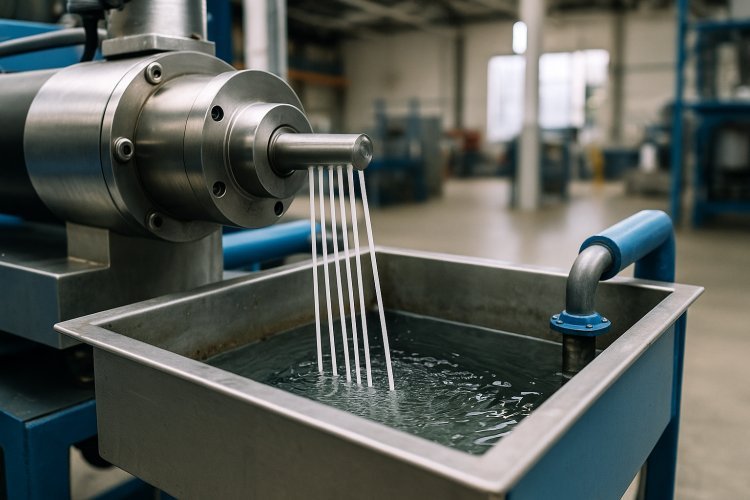
Pelletizing Systems
Pelletizing equipment converts extruded melt into uniform pellets. Strand pelletizers extrude material through a die into continuous strands that pass through a water bath for cooling before a rotating cutter dices them into pellets. This system provides operational flexibility and lower capital costs.
Underwater pelletizers cut molten polymer immediately as it exits the die face while submerged in process water. The instant cooling produces spherical pellets with excellent uniformity, ideal for high-quality color masterbatch production. Pellet sizes range from 0.5 mm micropellets to standard 3-4 mm granules.
Water-ring pelletizers offer a middle ground between strand and underwater systems, handling sticky materials and soft compounds effectively.
High-Speed Mixer
High-speed mixers prepare raw materials before extrusion by blending carrier resin pellets with pigment powders and additives. Intensive mechanical action generates frictional heat while distributing particles evenly. Temperature control prevents premature melting.
These mixers significantly improve pigment dispersion efficiency in the subsequent extrusion step. Pre-mixed batches enter the extruder with pigments already distributed among resin particles.
Cooling Systems
Cooling systems maintain product quality during and after pelletization. Water baths provide initial cooling for strand pelletizers, preventing thermal shock. Air knives remove surface moisture before vibration dryers achieve moisture levels below 0.2%. Proper cooling prevents pellet agglomeration and ensures a free-flowing product.
Screen Changer and Filter
Screen changers remove contaminants and gels from polymer melt before pelletization. Continuous screen changers allow filter replacement without stopping production, maximizing uptime. Mesh size selection balances filtration level against pressure drop.
Automated Control System (PLC/HMI)
Modern masterbatch lines integrate programmable logic controllers with human-machine interfaces for comprehensive process control. These systems manage recipe parameters, including temperatures, screw speeds, and feed rates across all equipment. Real-time monitoring displays critical process variables and alerts operators to deviations.
Recipe management capabilities store dozens of formulations for quick changeover between different masterbatch grades. Data logging creates production records for quality traceability and process optimization analysis. The industrial automation market reached USD 206.33 billion in 2024 [3], reflecting widespread adoption of smart manufacturing technologies.

Vacuum Degassing Unit
Vacuum degassing removes moisture, air, and volatile compounds trapped in polymer melt. Strategic port placement along the extruder barrel enables effective devolatilization without compromising mixing efficiency. Proper degassing prevents surface defects in finished pellets and improves dispersion quality.
| Equipment Type | Primary Function | Precision Level | Best Application |
| Co-rotating TSE | Compounding & mixing | High dispersion | All masterbatch types |
| Gravimetric Feeder | Material dosing | ±0.2% accuracy | High-value formulations |
| Underwater Pelletizer | Pellet formation | Spherical, uniform | Color masterbatch |
| Strand Pelletizer | Pellet formation | Cost-effective | Filler masterbatch |
| High-Speed Mixer | Pre-blending | Batch uniformity | Powder pigments |
| PLC/HMI System | Process control | Real-time monitoring | All production lines |
Specialized Equipment for Different Masterbatch Types
Different masterbatch categories require tailored equipment configurations. Color masterbatches demand exceptional dispersion quality and minimal contamination. Filler masterbatches need robust machinery for abrasive materials at high loading percentages. Additive masterbatches require precise temperature management for heat-sensitive compounds.
Color Masterbatch Production
Color masterbatch demands exceptional pigment dispersion for consistent color strength. Clamshell barrel designs simplify cleaning during color changeover, reducing downtime. High-shear mixing zones enhance wetting of pigment particles by carrier resin.
Production equipment choices impact the carbon footprint of color masterbatch manufacturing. Twin-screw extruders excel at processing white masterbatch containing TiO₂ for opacity and brightness, as well as black masterbatch with carbon black for UV protection.
Filler Masterbatch Equipment
Filler masterbatches containing high concentrations of CaCO₃, talc, or BaSO₄ require robust equipment with enhanced wear resistance. Hardened barrel liners extend service life when processing abrasive mineral fillers. High-torque extruders handle the increased viscosity of highly filled compounds.
Banbury mixers and kneader machines precondition filler compounds before twin-screw extrusion for improved dispersion. The combination produces filler masterbatches with uniform particle distribution throughout the carrier resin matrix.
Additive Masterbatch Systems
Additive masterbatches incorporating UV stabilizers, flame retardants, or antioxidants require lower processing temperatures to prevent thermal degradation. Gravimetric feeding ensures accurate dosing of expensive additive concentrates. Split-feed configurations introduce heat-sensitive additives downstream after initial carrier resin melting.
Selection Criteria for Masterbatch Manufacturing Equipment
Throughput rate requirements determine extruder size and auxiliary equipment capacity. Small-scale operations need 50-100 kg/h systems, while large facilities require 500+ kg/h production lines. Carrier resin compatibility affects material handling. PP and PE resins dominate as carrier polymers, though PET applications grow rapidly. L/D ratio selection balances mixing efficiency against equipment cost. Understanding processing requirements across the pulp and paper industry helps inform equipment specifications.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Wear resistance features extend equipment life in demanding applications. Replaceable barrel liners enable quick efficiency restoration. Cleaning procedures for color changeover impact production flexibility. Preventive maintenance schedules reduce unexpected downtime and extend equipment service life.

Conclusion
Selecting appropriate machines for masterbatch manufacturing requires understanding how each equipment type contributes to process efficiency and product quality. Twin-screw extruders, precision feeding systems, and advanced pelletizing equipment form the core of modern production lines. Equipment choices should align with production capacity needs and material specifications. Plentiful Choices provides comprehensive machinery solutions and technical expertise for masterbatch production line installations.
FAQ
What is the most important machine in masterbatch manufacturing? The twin-screw extruder performs the actual compounding and mixing of pigments or additives into carrier resin. Without proper extrusion, achieving uniform pigment dispersion becomes impossible.
How do I choose between underwater and strand pelletizers? Underwater pelletizers suit applications requiring spherical pellets with tight size distribution, particularly for color masterbatch. Strand pelletizers offer lower capital costs, ideal for filler masterbatches and cost-sensitive operations.
What L/D ratio is best for color masterbatch production? L/D ratios between 40 and 48 work well for color masterbatch manufacturing. Higher ratios provide additional mixing zones for thorough pigment dispersion.
Why are gravimetric feeders preferred over volumetric? Gravimetric feeders deliver ±0.2% dosing accuracy versus ±5% for volumetric systems. This precision reduces material waste and ensures consistent product quality.
How does automation improve masterbatch production efficiency? Automated control systems optimize process parameters in real-time, reduce human error, enable rapid recipe changeover, and provide production data for quality traceability.
References
[1] Grand View Research. (2024). Masterbatch Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/masterbatch-market
[2] Grand View Research. (2024). U.S. Twin Screw Extruders Market Size & Share Report. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/us-twin-screw-extruders-market-report
[3] Grand View Research. (2024). Industrial Automation and Control Systems Market Report. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/industrial-automation-market