TL;DR Summary
- Stone paper uses calcium carbonate (limestone) as the primary raw material, completely eliminating wood pulp dependency.
- Manufacturing requires zero water, chlorine, or bleaching chemicals throughout the entire production process.
- The process combines ultra-fine mineral powder with HDPE polymer through precision-blown film extrusion technology.
- Production creates waterproof, tear-resistant sheets that maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions.
- Environmental impact is 67% lower than conventional paper manufacturing, with zero deforestation and minimal energy consumption.
What Stone Paper Actually Is?
Stone paper represents a revolutionary approach to paper manufacturing that eliminates trees from the equation entirely. Understanding what stone paper is made of reveals how this innovative material uses abundant mineral resources as its foundation instead of traditional wood fibers.
The material consists of finely ground calcium carbonate particles bonded with high-density polyethylene resin and a small percentage of proprietary coating. This combination demonstrates how stone paper is made through advanced mineral processing techniques that create sheets possessing waterproof and tear-resistant properties that regular paper cannot match.
Raw Materials Required for Stone Paper Production
The stone paper manufacturing process begins with carefully selected stone paper raw materials that determine the final product’s quality and characteristics. Learning how to make paper from calcium carbonate requires understanding these essential components.
Primary Components
Calcium Carbonate (80%) Limestone serves as the backbone of stone paper production. Manufacturers source high-purity calcium carbonate, typically requiring particles processed through 1500-2500 mesh screens to achieve the ultra-fine consistency needed for smooth paper texture.
HDPE Polymer Binder (18%) High-density polyethylene acts as the binding agent that holds calcium carbonate particles together. This precise percentage ensures optimal flexibility and durability while maintaining the paper’s structural integrity.
Proprietary Coating (2%) The remaining composition includes specialized coatings that enhance printability, reduce static, and provide heat resistance during manufacturing and end-use applications.
Quality Control Standards
Production facilities maintain strict quality standards for raw materials. The calcium carbonate HDPE blend must meet specific purity requirements, with less than 0.1% impurities to prevent manufacturing defects or quality issues in the final product.
Step-by-Step Stone Paper Production Process
Understanding how stone paper is made requires examining each manufacturing stage that transforms raw limestone into usable paper sheets. This comprehensive step-by-step stone paper production guide reveals the precise methods behind this revolutionary material.

Stage 1: Material Preparation and Grinding
The limestone paper-making process begins with crushing large limestone rocks into progressively smaller pieces using industrial-grade crushing equipment. Specialized mills reduce the stone to powder form, achieving particle sizes that pass through 1500-2500 mesh screens to ensure optimal fineness.
This ultra-fine grinding creates particles measuring just 6-10 micrometers, ensuring the smooth paper texture without rough or gritty surfaces that would compromise print quality. Quality control teams continuously monitor particle size distribution using advanced laser diffraction analyzers to maintain consistency.
Stage 2: Mixing and Compounding
Manufacturers blend the calcium carbonate powder with HDPE resin using high-intensity mixers. The mixing process occurs at temperatures between 160-180°C, allowing the polymer to coat each mineral particle evenly.
Specialized compounding equipment creates a homogeneous mixture with consistent particle distribution. The process takes 15-20 minutes to ensure complete integration of all components.
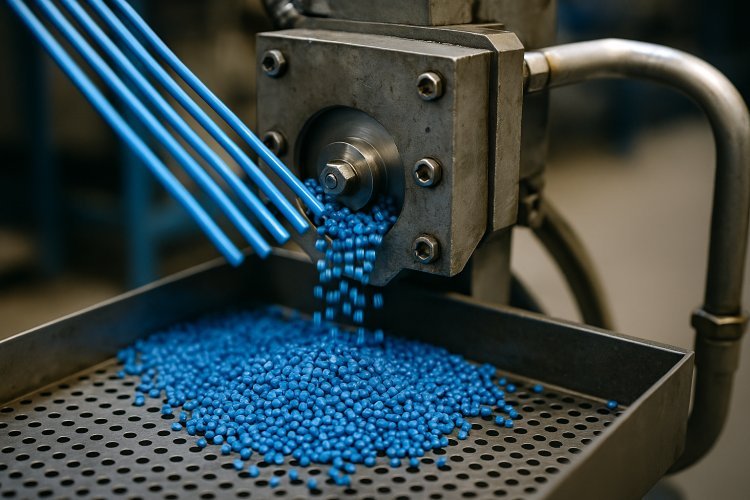
Stage 3: Extrusion Manufacturing
The blown film extrusion for stone paper represents the most critical production phase. Mixed materials enter extruder machines heated to 160°C, where they melt and form a continuous stream.
The molten mixture passes through calibrated dies that determine paper thickness. Most stone paper production line installations create sheets ranging from 0.1mm to 0.4mm in thickness, depending on intended applications.
Stage 4: Cooling and Calendering
Extruded sheets pass through cooling rollers that solidify the material while maintaining smooth surfaces. Calendering machines apply controlled pressure to achieve uniform thickness and desired surface finish.
This stage determines final paper characteristics, including opacity, smoothness, and print receptivity. Temperature control during cooling prevents surface defects and ensures consistent quality.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The stone paper environmental impact presents significant advantages over traditional papermaking methods that require extensive natural resources. With global paper consumption reaching 400 million tons in 2023, sustainable alternatives become increasingly critical.
Water Conservation Benefits
Traditional paper manufacturing consumes approximately 10-20 liters of water per sheet, while stone paper production requires zero water throughout the entire manufacturing process. This represents a 100% reduction in water consumption—an extraordinary achievement considering manufacturing facilities report complete elimination of wastewater treatment needs and environmental contamination risks.
The water savings become even more significant when considering scale: producing one ton of stone paper saves approximately 2 million liters of fresh water compared to conventional paper manufacturing, making it invaluable for water-stressed regions worldwide.
Carbon Footprint Analysis
Life cycle assessments show that stone paper production generates 67% fewer carbon emissions than wood pulp paper manufacturing. The elimination of tree harvesting, chemical processing, and water treatment significantly reduces the overall environmental footprint.
Energy consumption during stone paper production averages 2.3 kWh per kilogram, compared to 4.2 kWh for traditional paper manufacturing.
Stone Paper vs Traditional Paper Manufacturing
The difference between stone paper and wood pulp paper extends beyond raw materials to encompass entire production philosophies and environmental approaches. Comparing stone paper vs plastic also reveals significant advantages in both sustainability and performance characteristics.
Production Method Comparison
Traditional paper requires wood chips, extensive chemical processing, bleaching with chlorine, and massive water consumption. The process involves pulping, cleaning, bleaching, and forming—each stage generating environmental waste and requiring significant energy input.
Stone paper manufacturing eliminates chemical processing, bleaching agents, and water usage. The streamlined process reduces production complexity while creating superior product characteristics that demonstrate how stone paper is made without compromising quality or environmental responsibility.
Performance Characteristics
Wood pulp paper tears easily when wet, absorbs liquids readily, and degrades under moisture exposure. Stone paper maintains structural integrity when wet, resists tearing, and provides superior durability for demanding applications.
Print quality on stone paper exceeds traditional paper performance, with better ink adhesion and reduced bleeding or feathering effects.
Industrial Equipment and Production Lines
Modern stone paper production line installations require specialized equipment designed for mineral-based manufacturing processes.
Essential Machinery Components
High-Temperature Extruders Production lines utilize twin-screw extruders capable of processing calcium carbonate mixtures at temperatures up to 180°C. These machines feature specialized screws designed for mineral-filled polymers.
Blown Film Equipment: The blown film extrusion system creates continuous sheets with controlled thickness and width specifications. Advanced systems include automatic thickness monitoring and adjustment capabilities.
Quality Control Systems Integrated inspection systems monitor sheet thickness, surface quality, and opacity throughout production. Automated systems detect defects and trigger corrective actions to maintain consistent quality standards.
Production Capacity Planning
Modern stone paper line setup configurations achieve production rates between 200-500 kilograms per hour, depending on sheet thickness and width specifications. Large-scale facilities often install multiple production lines to meet market demand.
Quality Standards and Specifications
Stone paper manufacturing adheres to international standards that ensure consistent product quality and performance characteristics.
Physical Property Requirements
Manufactured stone paper must meet specific density requirements, typically ranging from 1.0-1.6 g/cm³. Tensile strength standards require minimum values of 25 MPa in the machine direction and 20 MPa in the cross direction.
Opacity levels must exceed 95% for writing applications, while thickness tolerances remain within ±5% of specified values throughout production runs.
Testing and Certification Protocols
Quality assurance teams conduct regular testing using standardized procedures. Tests include tensile strength measurement, opacity assessment, surface roughness evaluation, and print quality verification.
Manufacturers maintain detailed quality records demonstrating compliance with industry standards and customer specifications.
Applications and Market Uses
Stone paper production serves diverse markets requiring durable, waterproof paper alternatives with superior performance characteristics. Despite 68% of U.S. paper being recycled, specialized applications still require virgin materials with enhanced properties.
Commercial Applications
Packaging industries utilize stone paper for luxury product packaging, food containers, and moisture-resistant labels. The material’s grease resistance and durability make it ideal for demanding packaging applications.
Publishing companies increasingly adopt stone paper for premium publications, outdoor guides, and educational materials requiring water resistance.
Specialty Markets
Marine and outdoor industries rely on stone paper for charts, maps, and reference materials that must withstand harsh environmental conditions. The material’s tear resistance and waterproof properties provide reliability in challenging situations.
Recycling and End-of-Life Management
Understanding how to recycle stone paper requires recognizing its unique composition, which differs from traditional paper recycling processes. While the EPA reports paper recycling rates of 29.6% in their recent assessments, stone paper requires specialized handling.
Recycling Process Requirements
Stone paper recycling involves separating calcium carbonate from polymer binders through specialized processing techniques. The recovered calcium carbonate returns to manufacturing processes, while polymer components undergo separate recycling streams.
Current recycling systems achieve 85-90% material recovery rates, with both calcium carbonate and HDPE components finding new applications in various industries.
Biodegradability Characteristics
Is stone paper is biodegradable remains a complex question due to its mixed composition. The calcium carbonate component biodegrades naturally, returning to soil as limestone particles. The HDPE portion requires controlled composting conditions or recycling for proper disposal.
Future Developments in Stone Paper Manufacturing
Innovation in rich mineral paper manufacturing continues to advance production efficiency and environmental benefits. Multiple stone paper patents protect various manufacturing techniques and formulations, driving competitive development across the industry.
Technological Improvements
Research focuses on developing bio-based polymer alternatives to HDPE, potentially creating fully biodegradable stone paper variants. New extrusion technologies promise improved production speeds and energy efficiency that further demonstrate how stone paper is made more sustainably.
Advanced automation systems reduce labor requirements while improving quality consistency throughout production processes. These innovations show how stone paper is made with increasing precision and environmental responsibility.
Market Growth Projections
Industry analysts project 15-20% annual growth in stone paper demand as businesses prioritize sustainable alternatives to traditional paper products. Expanding applications in packaging, publishing, and specialty markets drive continued market development.
Conclusion
Stone paper manufacturing represents a paradigm shift toward sustainable paper production that eliminates trees, water, and harmful chemicals from the papermaking process. The innovative combination of calcium carbonate and polymer binding creates superior products while dramatically reducing environmental impact.
The step-by-step stone paper production process transforms abundant limestone resources into durable, versatile paper alternatives suitable for demanding applications. Understanding how stone paper is made reveals the sophisticated engineering behind this revolutionary material that positions itself as a cornerstone of sustainable industrial development as technology continues advancing and environmental awareness grows.
Frequently Asked Questions
Stone paper is an eco-friendly paper alternative made primarily from calcium carbonate (limestone) combined with HDPE polymer and proprietary coating, creating waterproof and tear-resistant sheets without using trees or water.
Stone paper uses mineral-based raw materials instead of wood fibers, requires no water during manufacturing, contains no bleaching chemicals, and provides superior durability, water resistance, and tear strength compared to traditional paper.
The main ingredient is calcium carbonate, comprising 80% of the material, derived from finely ground limestone that has been processed through 1500-2500 mesh screens for optimal consistency.
No, stone paper production requires zero water throughout the entire manufacturing process, eliminating wastewater generation and treatment requirements that burden traditional paper manufacturing.
Yes, stone paper demonstrates significant environmental benefits, including 67% lower carbon emissions, zero water consumption, no tree harvesting, and elimination of harmful chemicals used in conventional paper production.
Stone paper recycling involves specialized processing to separate calcium carbonate from polymer components, achieving 85-90% material recovery rates through dedicated recycling systems designed for mineral-based materials.